Integrity Constraints
- Attribute Constraints, e.g data types on columns
- Key Constraints, e.g primary keys
- Referential Integrity Constraints, enforced through foreign keys
Why Constraints?
- Constraints give the data structure
- Constraints help with consistency, and thus data quality
- Data quality is a business advantage / data science prerequisite
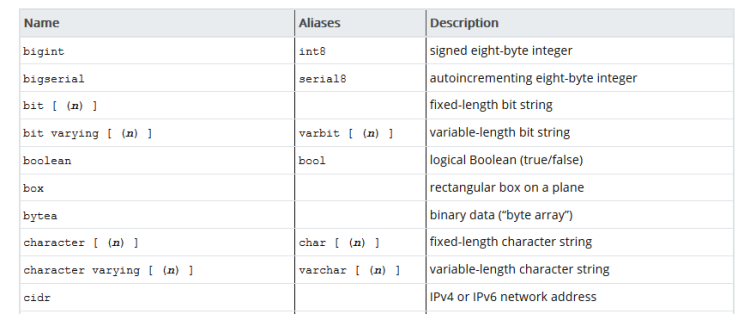
Data Types as Attribute Constraints
![a]()
Casting Data Types
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
CREATE TABLE weather( temperature integer, wind_speed text ); SELECT temperature * wind_speed AS wind_chill FROM weather;
The above sql statement results in error. Operator does not exist: integer * text
HINT: No operator matches the given name and argument type(s).
You might need to ass explicit type casts.1 2 3
SELECT temperature * CAST(wind_speed AS integer) AS wind_chill FROM weather;
Most Common Data Types
text: character strings of any lengthvarchar[(x)]: a maximum ofncharacterschar[(x)]: a fixed-length string ofncharactersboolean: can only take three states, e.g:TRUE,FALSEandNULLdate,timeandtimestamp: various formats for date and time calculationsnumeric: arbitray precision numbers, e.g:3.1457integer: whole numbers in the range of-2147483648and+2147483647
Creating columns with specific data types upon table creation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
CREATE TABLE students ( ssn integer, name varchar(64), dob date, average_grade numeric(3,2), --e.g 5.54 tuition_paid boolean );
- Alter types after table creation
1 2 3
ALTER TABLE students ALTER COLUMN name TYPE varchar(128);
1 2 3 4 5
ALTER TABLE students ALTER COLUMN average_grade TYPE integer -- Turns 5.54 into 6, not 5, before type conversion USING ROUND(average_grade)
Not-Null Constraints
- Disallow
NULLvalues in a certain column - Must hold true for the current state
- Must hold true for any future state
- Disallow
Adding a Not-Null Constraints
- While creating a table
1 2 3 4 5 6
CREATE TABLE students ( ssn integer not null, lastname varchar(54) not null, home_phone integer, office_phone integer );
- After the table has been created
1 2 3
ALTER TABLE students ALTER COLUMN home_phone SET NOT NULL;
- While creating a table
Removing a Not-Null Constraints
1 2 3
ALTER TABLE students ALTER COLUMN ssn DROP NOT NULL:
Unique Constraints
- Disallow duplicate values in a column
- Must hold true for the current state
- Must hold true for any future state
Adding UNIQUE Constraints
- While creating a table
1 2 3
CREATE TABLE table_name ( column_name UNIQUE )
- After the table has been created
1 2
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD CONSTRAINT some_name UNIQUE(column_name);
- While creating a table
Constraints
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.
Contents