Using Aggregation Functions Over Windows
Ranking Functions
ROW_NUMBER(): Unique, ascending integer value starting from 1.RANK(): Ascending integer value starting from 1. Can have ties. Can skip numbers.DENSE_RANK(): Ascending integer value starting from 1. Can have ties. Will not skip numbers.
Calculating Row Numbers
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
SELECT s.RunsScored, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY s.RunsScored DESC) AS rn FROM dbo.Scores s ORDER BY s.RunsScored DESC;
Calculating ranks and dense ranks
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
SELECT s.Runscored, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY s.RunsScored DESC) AS rk, DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY s.RunsScored DESC) AS dr FROM dbo.Scores s ORDER BY s.RunsScored DESC;
Partitions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
SELECT s.Team, s.RunsScored, ROW_NUMBER() OVEr (PARTITION BY s.Team ORDER BY s.RunsScored DESC) AS rn FROM dbo.Scores s ORDER BY s.RunsScored DESC:
Alaises for Multiple Window Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
SELECT id, account_id, standard_qty, DATE_TRUNC('month', occurred_at) AS month, DENSE_RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY account_id ORDER BY DATE_TRUNC('month', occurred_at)) AS dense_rank, SUM(standard_qty) OVER main_window AS sum_standard_qty, COUNT(standard_qty) OVER main_window AS count_standard_qty, AVG(standard_qty) OVER main_window AS avg_standard_qty, MIN(standard_qty) OVER main_window AS min_standard_qty, MAX(standard_qty) OVER main_window AS max_standard_qty FROM demo.orders WINDOW main_window AS (PARTITION BY account_id ORDER BY DATE_TRUNC('month', occurred_at))
Aggregate Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
SELECT s.Team, s.RunsScored, MAX(s.RunsScored) OVER (PARTITION BY s.Team) AS MaxRuns FROM dbo.Scores s ORDER By s.RunsScored DESC;
Aggregations with Empty Windows
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
SELECT s.Team, s.RunsScored, MAX(s.RunsScored) OVER() AS MaxRuns FROM dbo.Scores s ORDER BY s.RunsScored DESC;
Calculating Running Totals and Moving Averages
Running Totals
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
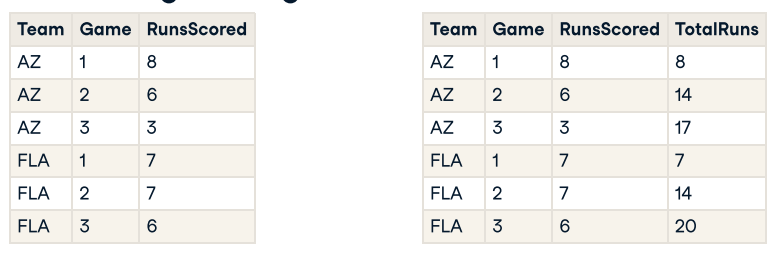
SELECT s.Team, s.Game, s.RunsScored, SUM(s.RunsScored) OVER(PARTITION BY s.Team ORDER BY s.Game ASC RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW ) AS TotalRuns FROM #Scores s;
![image]()
RANGE and ROWS
RANGE- Specify a range of results
- “Duplicates” processed all at once
- Only supports
UNBOUNDEDandCURRENT ROW
ROWS- Specify number of rows to include
- “Duplicates” processed a row at a time
- Supports
UNBOUNDED,CURRENT ROW, and number of rows
Calculating Moving Averages
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
SELECT s.Team, s.Game, s.RunsScored, AVG(s.RunsScored) OVER (PARTITION BY s.Team ORDER BY s.Game ASC ROWS BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW) AS AvgRuns From #Scores s;
Working with LAG() and LEAD()
The LAG() window function
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
SELECT dsr.CustomerId, dsr.MonthStartDate, LAG(dsr.NumberOfVisits) OVER(PARTITION BY dsr.CustomerID ORDER BY dsr.MonthStartDate) AS Prior, dsr.NumberOfVisits FROM dbo.DaySpaRollup dsr;
The LEAD() Window Function
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
SELECT dsr.CustomerId, dsr.MonthStartDate, dsr.NumberOfVisits, LEAD(dsr.NumberOfVisits) OVER (PARTITION BY dsr.CustomerID ORDER BY dsr.MonthStartDate) AS Next FROM dbo.DaySpaRollup dsr;
Specifying number of rows back
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
SELECT dsr.CustomerId, dsr.MonthStartDate, LAG(dsr.NumberOfVisits, 2) OVER (PARTITION BY dsr.CustomerID ORDER BY dsr.MonthStartDate) AS Prior2, LAG(dsr.NumberOfVisits,1) OVER (PARTITION BY dsr.CustomerID ORDER BY dsr.MonthStartDate) AS Prior1, dsr.NumberOfVisits FROM dbo.DaySpaRollup dsr;
![image]()
1 2 3 4 5
SELECT Date, LAG(Val,1) OVER (ORDER BY DATE) AS PriorVal, Val FROM t;
![image]()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
SELECT Date, LAG(Val,1) OVER (ORDER BY DATE) As PriorVal, Val FROM t WHERE t.Dat > '2019-01-02';
![image]()
Windows and filters and CTEs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
WITH records AS ( SELECT Date, LAG(Val,1) OVER (ORDER BY Date) AS PriorVal, VAL FROM t ) SELECT r.Date, r.PriorVal, r.Val FROM records r WHERE r.Date > '2019-01-02';