In a database, a view is the result set of a stored query on the data, which the database users can query just as they would in a persistent database collection object.
Virtual table that is not part of the physical schema
- Query, not data, is stored in memory
- Data is aggregated from data in tables
- Can be queried like a regular database table
No need to retype common queries or alter schemas
Creating A View
Syntax:
1 2 3 4 5
CREATE VIEW view_name AS SELECT col1, col2 FROM table_name WHERE condition;
![image]()
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
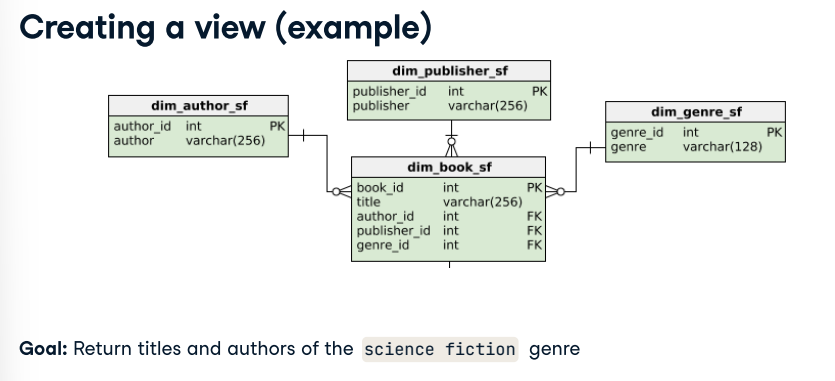
CREATE VIEW scifi_books AS SELECT title, author, genre FROM dim_book_sf JOIN dim_genre_sf ON dim_genre_sf.genre_id = dim_book_sf.genre_id JOIN dim_author_sf ON dim_author_sf.author_id = dim_book_sf.author_id WHERE dim_genre_sf.genre = 'science fiction';
Querying a view (example)
1
SELECT * FROM scifi_books
Viewing Views
1
SELECT * FROM information_schema.views;
Includes system views
1 2
SELECT * FROM information_schema.views WHERE table_schema NOT IN ('pg_catalog', 'information_schema');
Excludes system views
Benefits of Views
- Doesn’t take up storage
- A form of access control
- Hide sensitive columns and restrict what user can see
- Masks complexity of queries
- Useful for highly normalized schemas
Managing Views
Creating more complex views
- Aggregation:
SUM(),AVG(),COUNT(),MIN(),MAX(),GROUP BY, etc. - Joins:
INNER JOIN,LEFT JOIN,RIGHT JOIN,FULL JOIN - Conditionals:
WHERE,HAVING,UNIQUE,NOT NULL,AND,OR,>,<, etc.
- Aggregation:
Granting and revoking access to a view
GRANT privilege(s) or REVOKE privilege(s)
ON object
TO roleorFROM role- Privileges:
SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE, etc. - Objects: table, view, schema, etc.
- Roles: a database user or a group of database users
- Privileges:
Granting and Revoking Example
1
GRANT UPDATE ON ratings TO PUBLIC;
1
REVOKE INSERT ON films FROM db_user;
Updating a view
1
UPDATE films SET kind='Dramatic' WHERE kind='Drama';
Not all views are updatable
- View is made up of one table
- Doesn’t use a window or aggregate function
Inserting into a view
1 2
INSERT INTO films (code, title, did, date_prod, kind) VALUES('T_601', 'Yojimbo', 106, '1961-06-16', 'Drama');
Not all views are insertable
Note: AvoiD Modifying Data Through Views
Dropping a view
1
DROP VIEW view_name [ CASCADE | RESTRICT ];
RESTRICT(default): returns an error if there are objects that depend on the viewCASCADE: drops view and any object that depends on that view
Redefining a view
1
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW view_name AS new_query
- If a view with
view_nameexists, it is replaced new_querymust generate the same column names, order, and data types as the old query- The column output may be different
- New columns may be added at the end
If these criteria can’t be met, drop the existing view and create a new one
- If a view with
Altering a view
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name ALTER [ COLUMN ] column_name SET DEFAULT expression ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name ALTER [ COLUMN ] column_name DROP DEFAULT ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name OWNER TO new_owner ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name RENAME TO new_name ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name SET SCHEMA new_schema ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name SET ( view_option_name [=view_option_value] [,...]) ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name RESET (view_option_name [,...])
Materialized Views
Two Types of Views
- Views
- Also known as non-materialized views
- Materialized Views
- Physically Materialized
- Stores the query results, not the query
- Querying a materialized view means accessing the stored query results
- Not running the query like a non-materialized view
- Refreshed or rematerialized when prompted or scheduled
- Views
When to use materialized views
- Long running queries
- Underlying query results don’t change often
- Data warehouses because OLAP is not write-intensive
- Save on computational cost of frequent queries
Implementing materialized views
1 2 3
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW my_mv AS SELECT * FROM existing_table; REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW my_mv;
Managing dependencies
- Materialized views often depend on other materialized views
- Creates a dependency chain when refreshing views
- Not the most efficient to refresh all views at the same time
Tools for Managing Dependencies
- Use Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) to keep track of views
- Pipeline scheduler tools like:- Apache Airflow, Luigi