Advantages of Triggers
- Used for database integrity
- Enforece business rules directly in the database
- Control on which statements are allowed in a database
- Implementatino of complex business logic triggered by a single event
- Simple way to audit databases and user actions
Disadvantages of Triggers
- Difficult to view and detect
- Invisible to client applications or when debugging code
- Hard to follow their logic when troubleshooting
- Can become an overhead on the server and make it run slower
Finding server-level triggers
1
SELECT * FROM sys.server_triggers;
Finding database and table triggeers
1
SELECT * From sys.triggers;
Viewing a trigger definition (option 1)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
CREATE TRIGGER PreventOrdersUpdate ON Orders INSTEAD OF UPDATE AS RAISERROR ('Updates on "Orders" table are not permitted. Place a new order to add new products.', 16, 1);
Viewing a trigger definition (option 2)
1 2 3
SELECT definition FROM sys.sql_modules WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID ('PreventOrdersUpdate');
Viewing a trigger definition (option 3)
1
SELECT OBJECT_DEFINITION (OBJECT_ID ('PreventOrdersUpdate'));
Viewing a trigger definition (option 4)
1
EXECUTE sp_helptext @objanem = 'PreventOrderUpdate';
Use Cases For After Triggers (DML)
Keeping a history of row changes
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
CREATE TRIGGER CopyCustomersToHistory ON Customers AFTER INSERT, UPDATE AS INSERT INTO CustomersHistory (Customer, ContractId, Address, PhoneNo) SELECT Customer, ContractID, Address, PhoneNo, GETDATE() FROM inserted;
Table auditing using triggers
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
CREATE TRIGGER OrdersAudit ON Orders AFTER INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE AS DECLARE @Insert BIT = 0 , @Delete BIT = 0; IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM inserted) SET @Insert = 1; IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM deleted) SET @Delete = 1; INSERT INTO [TablesAudit] ([TableName], [EventType], [UserAccount], [EventDate]) SELECT 'Orders' AS [TableName] ,CASE WHEN @Insert = 1 AND @Delete = 0 THEN 'INSERT' WHEN @Insert = 1 AND @Delete = 1 THEN 'UPDATE' WHEN @Insert = 0 AND @Delete = 1 THEN 'DELETE' END AS [Event] ,ORIGINAL_LOGIN() ,GETDATE();
Notifying Users
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
CREATE TRIGGER NewOrderNotification ON Orders AFTER INSERT AS EXECUTE SendNotification @RecipientEmail = 'sales@freshfruit.com', @EmailSubject = "New order place", @EmailBody = 'A new order was just placed.';
Use cases for INSTEAD OF triggers (DML)
General use of INSTEAD OF triggers
- Prevent operations from happening
- Control database statements
- Enforce data integrity
Triggers that prevent changes
1 2 3 4 5
CREATE TRIGGER PreventProductChanges ON Products INSTEAD OF UPDATE AS RAISERROR ('Updates of products are not permitted. Contact the database administrator if a change is needed.', 16, 1);
Triggers that prevent and notify
```sql CREATE TRIGGER PreventCustomersRemoval ON Customers INSTEAD OF DELETE AS DECLARE @EmailBodyText NVARCHAR(50) = (SELECT ‘User “’ + ORIGINAL_LOGIN() + ‘” tried to remove a customer from the database.’); RAISERROR (‘Customer entries are not subject to removal.’, 16, 1);
1 2 3 4
EXECUTE SendNotification @RecipientEmail = 'admin@freshfruit.com' ,@EmailSubject = 'Suspicious database behavior' ,@EmailBody = @EmailBodyText; ```Triggers with Conditional Logic
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
CREATE TRIGGER ConfirmStock ON Orders INSTEAD OF INSERT AS IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM Products AS p INNER JOIN inserted AS i ON i.Product = p.Product WHERE p.Quantity < i.Quantity) RAISERROR ('You cannot place orders when there is no product stock.', 16, 1); ELSE INSERT INTO dbo.Orders (Customer, Product, Quantity, OrderDate, TotalAmount) SELECT Customer, Product, Quantity, OrderDate, TotalAmount FROM inserted;
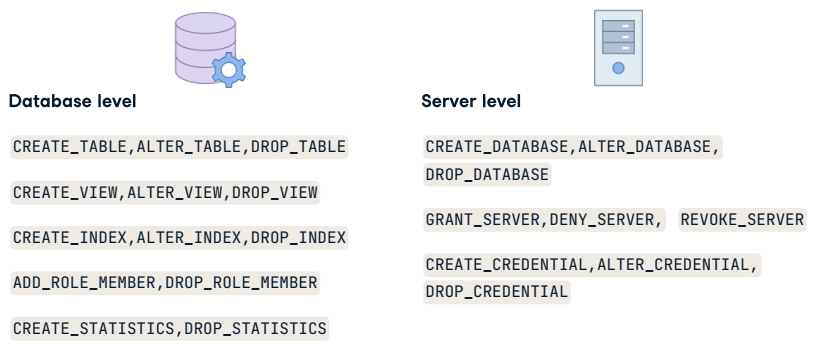
Use Cases for DDL Triggers
DDL trigger capabilities
![image]()
Database Auditing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
CREATE TRIGGER DatabaseAudit ON DATABASE FOR DDL_TABLE_VIEW_EVENTS AS INSERT INTO [DatabaseAudit] ([EventType], [Database], [Object], [UserAccount], [Query], [EventTime]) SELECT EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/EventType)[1]', 'NVARCHAR(50)'), EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/DatabaseName)[1]', 'NVARCHAR(50)'), EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/ObjectName)[1]', 'NVARCHAR(100)'), EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/LoginName)[1]', 'NVARCHAR(100)'), EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/TSQLCommand/CommandText)[1]', 'NVARCHAR(MAX)'), EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/PostTime)[1]', 'DATETIME');
Preventing Server Changes
1 2 3 4 5 6
CREATE TRIGGER PreventDatabaseDelete ON ALL SERVER FOR DROP_DATABASE AS PRINT 'You are not allowed to remove existing databases.'; ROLLBACK;