- Inside the linux terminal:-
- the
$represents the normal user - the
#represents the root or admin user
- the
To check the hostname we can use the
hostnamecommand For Eg:-1 2 3 4
``` Input: hostname Output: {returns the hostname} ```To check the current logged in user we can use the
whoamicommand For Eg:-1 2 3 4
``` Input: whoami Output: {returns the current logged in user} ```- To check the IP on Linux we can use the
ip addrcommandIP address is an unique address that identifies a device on the internet or a local network
For Eg:-
1 2 3 4
``` Input: ip addr Output: {returns the ip address} ``` To print out the working directory we can use the
pwdcommand For Eg:-1 2 3 4
``` Input: pwd Output: {prints the working directory} ```To make a folder on linux we can use the
mkdircommand For Eg:-1 2 3
``` Input: mkdir {directory_name} ```To change location or to move to another directory we can use the
cdcommand For Eg:-1 2 3
``` Input: cd {directory_name} ```To move back to another directory we can use the
cdcommand For Eg:-1 2 3
``` Input: cd .. ```
Here, the
..means that we should move one step back.To clear the screen we use the
clearcommand For Eg:-1 2 3
``` Input: clear ```
- To search for our folder/file inside a specific location we can use the
findcommandTo search for folder For Eg:-
1 2 3
``` Input: find path -name {folder/directory name} ```To search for file For Eg:-
1 2 3
``` Input: find . -type f -name {filename} ```
We can also use the
locatecommand for finding files or folders To create a file we can use the
touchcommand For Eg:-1 2 3
``` Input: touch {file_name} ```- Removing a directory
To remove or delete a directory we can use the
rmdircommand For Eg:-1
Input: rmdir {directory_name}To remove the directory and all the other files inside of it. For Eg:-
1
Input: rm -r {directory_name}
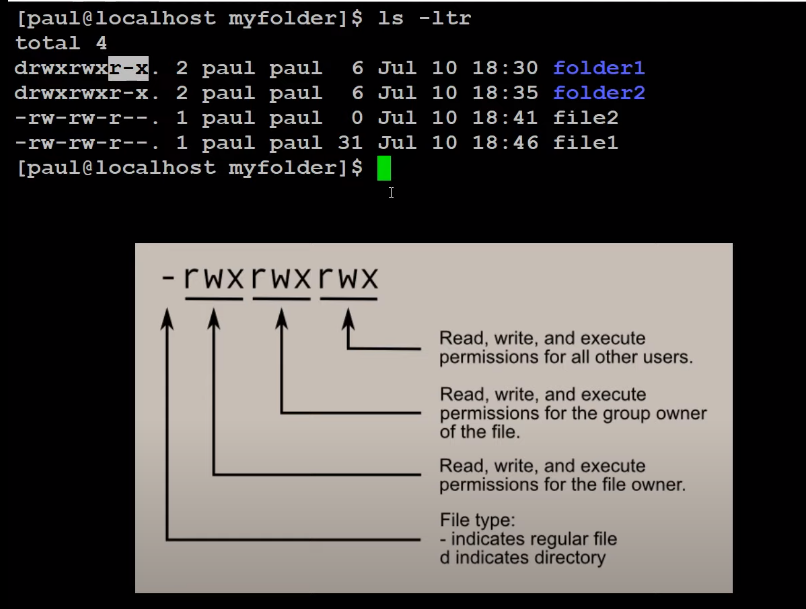
To view more information about the files we can use the
ls -ltrcommand For Eg:-1
Input: ls -ltr
Here, the
-lmeans we use a long listing format.-tmeans we sort by time, newest first, and-rmeans in the reverse order while sorting.![img]()
To view more information about the command we can use either the
mancommand or the--helparguement For Eg:-1 2 3
Input: ls --help OR Input: man lsTo edit or write into a file we can use the
vieditor. For Eg:-1
Input: vi {file_name}To start editing we need to go to
insertmode for which we must pressikey. Then we can insert the text as we like. To escape from the insert mode we can press theescapekey. Now, to save the file, we can press:wqwhere wq means save and quit.To print the file content into the shell we use
catcommand. For Eg:-1
Input: cat {file_name}- To count the no.of words and lines we use the
wccommand.To count only the no of lines we use
wc -lFor Eg:-1
Input: wc -l {file_name}
To compare two files we use the
diffcommand. For Eg:-1 2 3
``` Input: diff {file_1} {file_2} ```To compree and decompress files We use the
tardo to the packaging of files. For Eg:-1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
``` Input: tar {options} {tar_file_name} {file_1} {file_2} Eg: tar cvf files.tar file1 file2 Output: files.tar ``` Now, we need to compress the files.tar using the `gzip` command For Eg:- ``` Input: gzip {tar_file} Eg:- gzip files.tar Output: files.tar.gz ```Now, to decompress the compresseed file we use the
gunzipcommand For Eg:-1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
``` Input: gunzip {zipped_file} Eg:- gunzip gzip files.tar.gz Output: files.tar ``` And lastly, we need to untar the tar files For Eg:- ``` Input tar xvf {tar_file} Eg:- tar xvf files.tar Output: file1, file2s ```To copy file rom one folder to another we use the
cpcommand. For Eg:-1 2
Input: cp {source_file} {destination_path} Eg:- cp files.tar.gz folder1/To rename a file we use the
mvcommand For Eg:-1 2 3 4
``` Input: mv {old_file_name} {new_file_name} ``` Here, what we do is move the contents of the old file to the new file with a new name and then delete the old file. In linux, we use such indirect renaming of a file.- To split and combine the files
To combine a file For Eg:- Let’s suppose we want to create a new file-
filecwith the contents of two different files:fileaandfileb. To do this we use the>operator. For Example:-1 2 3
``` Input: cat filea fileb > filec ```To split a file For Eg:- Let’s suppose we want to split the content of a
fileainto two filesfilebandfilecthen we use thesplitcommand. For Example:-1 2 3
``` Input: split -l 1 filea ```
To search for words in a file and show them in a console we use the
grepcommand For Example:-1
Input cat {file_name} | grep {word}Here, the
|is the pipe operator which is used to chain the operations. Here, the ‘cat {file_name}’ returns some output, and its output is sent as an input to the ‘grep {word}` command.To read the start and end of the files we use the
headandtailcommand respectively For Example:-1 2 3 4 5 6
``` Input: head -2 {filename} Output: prints the first two line from the file. Input: tail -2 {filename} Output: prints the last two line from the file. ```To sort the file we use the
sortcommand For Example:-1
Input: sort {file_name}To prin only the unique value we use the
uniqcommand For Example:-1
Input: sort {file_name} | uniq
Basic Linux Commands
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.